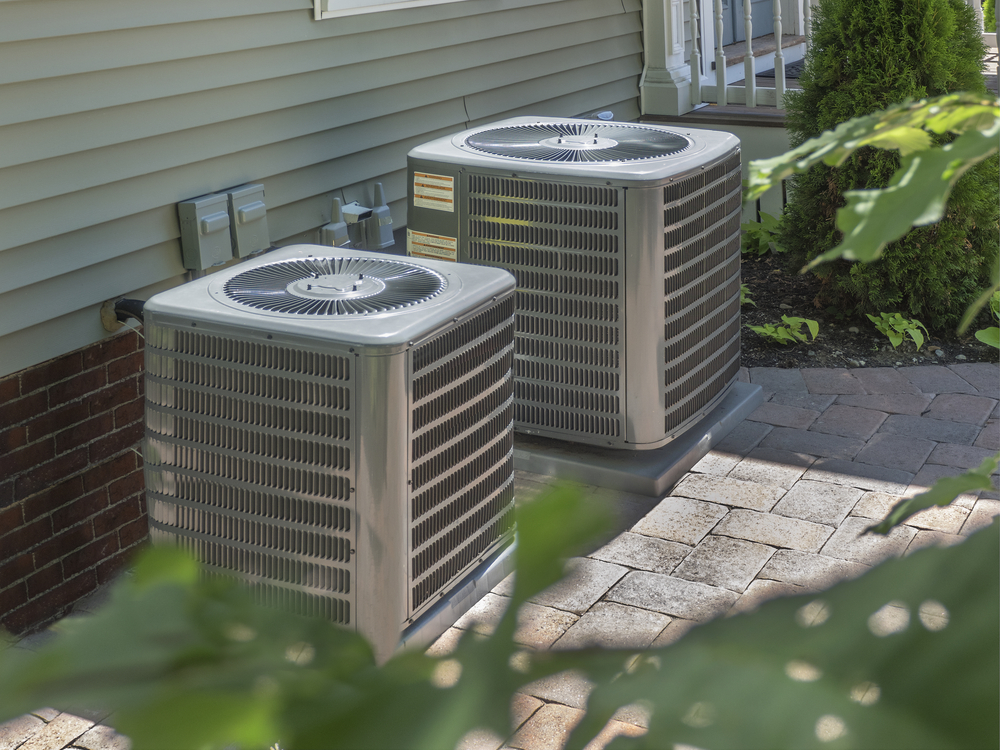
If you’ve ever wondered how a 2 zone HVAC system works, you’re in the right place. These innovative HVAC systems provide a smart way to manage the temperature in distinct areas of your home, potentially improving your indoor air quality. They can help you save money on utility bills and enhance overall comfort. Let’s explore the mechanics and benefits of 2 zone HVAC systems.
What Is a 2 Zone HVAC System?
A 2 zone HVAC system, also known as a dual-zone HVAC system, effectively divides your home into two separate areas, or “zones,” for heating and cooling purposes. Each of these zones is equipped with its own thermostat, granting independent temperature control over that specific area. This setup allows for customizable heating and cooling, catering to different needs within the same household.
The primary advantage of zoned HVAC systems is the ability to maintain different temperatures in various parts of your home simultaneously. This is particularly beneficial if you have sections of your house that are naturally harder to heat or cool, such as a sun-drenched room or a chilly basement. It’s also an excellent solution if family members have different temperature preferences, ensuring everyone remains comfortable in their respective spaces, potentially even making one room warmer than another.
Many homeowners with a two-story house find dual-zone HVAC systems particularly useful, as upstairs areas often become warmer than downstairs. By creating multiple zones, you can address these temperature discrepancies directly. This targeted approach not only boosts comfort but also contributes to more efficient energy use by the air conditioner or heat pump.
How Does a 2 Zone HVAC System Work?
The core of a 2 zone HVAC system’s operation lies with the zone control panel, a central processing unit that orchestrates the heating and cooling. This panel intelligently manages the flow of conditioned air—either cool air or warm air—to each designated temperature zone. It achieves this by working in conjunction with dampers strategically placed within your home’s ductwork, directing air precisely where it’s needed.
Here’s a more detailed step-by-step explanation of the process involved in how HVAC zoning functions:
- You, the homeowner, set your desired temperature for each zone using its dedicated thermostat. Modern smart thermostat options can even learn your preferences over time.
- These thermostats continuously monitor the ambient temperature in their respective zones and transmit this information, along with your setpoint, to the zone control panel.
- The control panel analyzes the data from all thermostats. It then determines which specific zones require heating or cooling to reach or maintain the ideal temperature.
- Based on this determination, the panel sends signals to motorized dampers installed within the ductwork. These dampers control the airflow by opening to allow conditioned air into a zone or closing to restrict it.
- Simultaneously, the control panel signals your main HVAC equipment (like a furnace, heat pump, or air conditioner) to turn on and produce either heated or cooled air. This conditioned air is then distributed only to the zones that currently need it, as dictated by the open dampers.
This entire process operates automatically once the system is configured, providing seamless temperature management. You don’t need to perform any manual adjustments to ducts or vents; the zone hvac system handles the distribution of warm air or cool air efficiently. The intelligent operation ensures that energy isn’t wasted on conditioning unoccupied or already comfortable areas.
Key Components of a 2 Zone HVAC System
To fully grasp how a 2 zone HVAC system works, it’s helpful to understand its principal components and their roles. These parts work together to deliver precise temperature control and efficiency for your indoor air.
1. Thermostats
Each zone within a zoned HVAC system is equipped with its own thermostat, which may include multiple sensors for greater accuracy. These devices are crucial as they allow you to set the specific temperature for that particular area. Beyond just setting temperature, many modern thermostats also measure current humidity levels, providing comprehensive data to the system.
This information is vital for the system to decide when to activate or deactivate heating or cooling for that zone. Options range from basic digital thermostats to advanced smart thermostat models that offer features like remote access, scheduling, and energy usage reports, further enhancing your ability to control temperature effectively.
2. Zone Control Panel
The zone control panel is effectively the brain of the dual-zone HVAC system. It receives input signals from all the thermostats in the different zones and acts as the central command for the entire HVAC work. Its primary function is to interpret these signals and then direct the operation of the dampers and the main HVAC units.
The panel ensures that heating and cooling efforts are coordinated and efficient. For instance, it manages calls for heating or cooling from different zones, ensuring your single heat pump or air conditioner isn’t overworked or trying to perform conflicting tasks. Advanced panels can also manage multi-stage equipment for even finer control.
3. Dampers
Dampers are essential mechanical components installed within your home’s ductwork; these modulating dampers act much like valves. Their job is to open and close to precisely control the flow of conditioned air to each specific temperature zone. When a zone doesn’t require heating or cooling, the control panel signals the damper for that zone to close, effectively blocking air from entering it.
Conversely, when a zone needs conditioning, its damper opens, allowing the warm air or cool air to flow freely. The dampers control airflow with precision, which is fundamental to the system’s ability to create different temperature environments. Proper installation and sealing of these dampers are critical for the efficiency of zone hvac systems.
4. Bypass Damper
A bypass damper is a specialized component crucial for maintaining the health and efficiency of your HVAC system, particularly in zoned setups. When some zones are closed off and don’t require air, the overall airflow from your air conditioner or furnace can create excess pressure within the ductwork. The bypass damper is designed to alleviate this.
It opens automatically to redirect this surplus air away from the closed zones and typically back into the return air duct of the HVAC system. This helps to maintain balanced air pressure, preventing strain on the blower motor, reducing noise, and ensuring your HVAC units operate smoothly and efficiently. Without a properly functioning bypass damper, the system could suffer from reduced performance and potential damage.
Benefits of a 2 Zone HVAC System
Now that we have a clearer picture of how a 2 zone HVAC system works, let’s explore the compelling advantages these zoned hvac systems offer homeowners. These benefits often lead to a more comfortable and cost-effective home environment.
Energy Savings
One of the most significant advantages of dual-zone HVAC systems is the potential for substantial energy savings. By allowing you to heat or cool only the areas of your home that are currently in use, you avoid wasting energy on conditioning empty rooms or seldom-used spaces. This targeted approach means your air conditioner and heating system run less frequently or at lower capacities, directly translating into lower monthly utility bills and helping you save money over time.
This efficiency is especially noticeable in larger homes or those with varied occupancy patterns throughout the day. The ability to control temperature independently in different zones prevents the common issue of over-conditioning some areas to make others comfortable, reducing overall energy consumption for your HVAC systems.
Improved Comfort
Different areas of your home naturally have varying temperature needs, and individual preferences for warmth or coolness can also differ among family members. A 2 zone HVAC system, or one with multiple zones, directly addresses this by allowing for customizable heating in each distinct zone. Whether it’s keeping the living room cool during the day and bedrooms comfortably warm at night, or accommodating someone who prefers a cooler office, these systems enhance personal comfort.
This level of control ensures that everyone in the household can enjoy their space at their preferred ideal temperature. No more arguments over a single thermostat setting for the entire house; each zone can be an oasis of comfort.
Better Temperature Control
Many homes have “problem areas”—rooms that are persistently too hot in the summer or too cold in the winter, regardless of the thermostat setting. This could be a sunroom, a room over the garage, or a finished basement. A dual zone hvac system, or systems with even more temperature zones, offers superior temperature control to balance out these inconsistencies.
By delivering conditioned air directly to where it’s needed and restricting it from areas that are already comfortable, these systems can overcome the challenges posed by home design, sun exposure, or insulation differences. This leads to more uniform and pleasant temperatures throughout your entire home, ensuring every room is usable and comfortable year-round. Effective air quality management is also a byproduct of better circulation control.
Reduced Wear and Tear
When your central HVAC system isn’t constantly working at full capacity to heat or cool your entire house, it experiences less strain. A 2 zone HVAC system, by design, reduces the overall workload on your HVAC equipment, such as your heat pump or air conditioner. This gentler operation can lead to a longer lifespan for your system components.
Consequently, you might find yourself needing fewer instances of air conditioning repair or furnace repair over the years. The reduced operational stress not only extends the life of your HVAC units but can also contribute to more consistent performance and lower maintenance costs, protecting your investment in your home’s comfort systems. This is a key benefit of effective hvac zoning.
Installing a 2 Zone HVAC System
If the way a 2 zone HVAC system works appeals to you, understanding the installation process is the next step. Implementing hvac zoning is a more involved task than setting up a standard, single-zone HVAC system.
Due to the complexity, installing a dual-zone air conditioner setup or a heating system with zones is generally not a do-it-yourself project. It requires the expertise of a qualified HVAC technician who understands ductwork modification, electrical wiring for the control panel and thermostats, and system balancing. These professionals ensure your zone heat and cool air distribution function correctly.
The installation process typically includes:
- Careful assessment of your home’s layout and existing ductwork to plan zone boundaries.
- Installing motorized dampers at strategic points within your ductwork. This often involves cutting into and sealing existing ducts.
- Mounting and wiring the zone control panel, which acts as the central hub.
- Installing and wiring new thermostats in each designated zone. This might involve running new wires if existing ones are insufficient.
- Connecting the zone control panel to your existing HVAC equipment, like your furnace or heat pump.
- Configuring and calibrating the entire system, including setting up the bypass damper if needed, to ensure optimal airflow and temperature control across all multiple zones.
The cost and complexity of installing zone hvac systems can vary significantly based on your home’s specific architecture, the current state of your HVAC system, and the type of equipment chosen. It’s often more straightforward and cost-effective to incorporate zoning during a new HVAC system installation or a furnace replacement. However, retrofitting an existing system with zoning is also feasible, though it may require more extensive ductwork modifications.
Some homeowners also consider options like ductless air conditioning for individual rooms if extensive duct modification for a full dual-zone air system is impractical. Always consult with experienced HVAC professionals to discuss the best approach for your home and to ensure proper furnace installation or modifications.
Maintenance for 2 Zone HVAC Systems
To ensure your 2 zone HVAC system continues to work efficiently and reliably, providing consistent comfort and energy savings, regular maintenance is essential. Proper upkeep can prevent common issues and extend the lifespan of your entire HVAC system, including specialized components like dampers and control panels.
Here are some important maintenance tips:
- Change your air filters regularly, typically every 1-3 months, depending on your filter type and home environment. Clean filters are crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality and allowing your system to run efficiently without strain.
- Schedule an annual professional inspection. A qualified technician can thoroughly check all components, including the thermostats, zone control panel, dampers, wiring, and your main HVAC units (air conditioner, heat pump, furnace). This proactive service can catch minor issues before they become major problems requiring costly furnace repair or air conditioning repair.
- Keep the area around your outdoor HVAC unit clear of leaves, grass clippings, shrubs, and other debris. Adequate airflow around the unit is vital for it to dissipate heat (in cooling mode) or absorb heat (in heating mode) effectively. This is a simple but important part of air conditioning maintenance and heat pump maintenance.
- Periodically check your thermostats. Ensure they have fresh batteries if applicable, are reading the room temperature accurately, and that their settings haven’t been inadvertently changed. A malfunctioning smart thermostat can disrupt the entire system.
- Listen for any unusual noises from your ductwork or HVAC equipment. Sounds like whistling, banging, or excessive rattling can indicate issues with dampers, air pressure, or loose components. Addressing these early can prevent further damage.
- Ensure ductwork is properly sealed. Leaky ducts can significantly reduce the efficiency of any HVAC system, especially a zoned one, as conditioned air might not reach the intended temperature zone. Leak detection services can help identify these problems.
Consistent heater maintenance and overall system care for your zoned HVAC will ensure it provides years of comfortable, efficient heating and cooling. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency, higher utility bills, and a greater likelihood of breakdowns, potentially requiring services like heat pump repair or extensive conditioning repair.
While focusing on your HVAC, remember that overall home efficiency contributes to lower monthly utility costs. Consider energy-efficient appliances, proper insulation, and even efficient water heaters, such as a tankless water heater. Some HVAC companies also offer services like water heater maintenance or tankless water heater maintenance, recognizing the interconnectedness of home energy systems. Proper maintenance across all systems, including furnace maintenance, ensures a comfortable and cost-effective living environment.
Common Issues with 2 Zone HVAC Systems
While 2 zone HVAC systems offer numerous advantages for controlling your home’s climate and improving indoor air, like any complex mechanical system, they can occasionally experience issues. Understanding these common problems can help you identify them early and seek appropriate solutions, often from a professional specializing in HVAC systems.
Uneven Heating or Cooling
One of the primary reasons for installing a zoned system is to combat uneven temperatures, so it’s frustrating if a zone is consistently too hot or too cold. This could stem from several issues: a malfunctioning damper that isn’t opening or closing fully, a faulty thermostat providing incorrect readings for that temperature zone, or even undersized ductwork for a particular area. An HVAC professional can diagnose the specific cause, which might involve checking the modulating dampers or ensuring the dampers control airflow correctly.
Short Cycling
Short cycling describes a condition where your HVAC system (air conditioner or heat pump) turns on and off much more frequently than it should, running for only short bursts. This can be caused by an HVAC system that’s oversized for the actual heating or cooling load of the zones calling for air. It might also indicate a problem with the bypass damper setup, which isn’t correctly managing excess air pressure, or restricted airflow due to dirty filters or blocked vents. Short cycling is inefficient, increases wear on components, and can lead to premature hvac units failure.
Thermostat Issues
Since each zone relies on its thermostat, problems with these devices can significantly impact system performance. Thermostat malfunctions can include incorrect temperature readings, loss of calibration, faulty wiring connections to the zone control panel, or dead batteries in battery-powered models. Even the placement of a thermostat (e.g., in direct sunlight or near a heat source) can cause inaccurate readings, leading to poor comfort control in that specific zone. A smart thermostat may require specific troubleshooting steps.
Noise from Ductwork
Unusual noises emanating from your vents or ductwork, such as whistling, humming, or a loud rushing sound, can be indicative of air pressure problems within your 2 zone HVAC system. This might occur if the ductwork is not sized correctly for the airflow, if dampers are not opening or closing smoothly, or if the bypass damper is not functioning as intended. These noises not only are annoying but can also signal inefficiency or strain on your system, affecting how your HVAC work is performed.
If you observe any of these common problems with your zone hvac, or other issues like a complete lack of cool air or warm air in one zone, it’s generally best to contact a qualified HVAC service professional. They have the diagnostic tools and expertise to accurately identify the root cause and perform necessary repairs, whether it’s a simple thermostat adjustment, damper repair, or more complex work on the control panel or HVAC units. Prompt attention to issues can prevent more significant damage and maintain the efficiency of your dual-zone air system, avoiding extensive air conditioning repair or heater repair.
Sometimes, what seems like an HVAC issue could be related to other systems. While HVAC technicians focus on air conditioning and heating, comprehensive home service providers might also handle furnace repair alongside plumbing repair or water heater repair. Maintaining all home systems, including ensuring your sump pumps are working and water lines are intact, contributes to a well-functioning home. Some even offer boiler repair or boiler installation for different types of heating systems.
Is a 2 Zone HVAC System Right for You?
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of how a 2 zone HVAC system works, including its components and benefits, you might be wondering if this type of HVAC zoning is a suitable investment for your home. A dual-zone HVAC system isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, but it shines in particular situations, significantly enhancing comfort and potentially reducing monthly utility bills.
Consider if any of these scenarios apply to your living situation:
- You live in a multi-story house. Heat naturally rises, often making upper floors uncomfortably warm while lower floors remain cool. A 2 zone system allows you to manage these distinct temperature needs independently, for example, keeping the upstairs cooler in summer.
- Your home features large, open-plan living areas combined with smaller, separate bedrooms. The heating and cooling requirements for a spacious living room can be very different from those of a compact bedroom, making independent control valuable.
- You have a finished basement or a converted attic space. These areas often have different insulation levels and exposure than the main living areas, making them difficult to keep comfortable with a single thermostat. Creating a separate temperature zone for them is ideal.
- Your house includes additions, sunrooms, or rooms with many windows. These spaces can experience significant temperature swings due to solar gain or heat loss, benefiting greatly from dedicated zone control for consistent comfort.
- Family members have notably different temperature preferences. A zoned system can end thermostat wars by allowing, for instance, a cooler setting in one zone (like a home office) and a warmer setting in another (like a child’s bedroom), ensuring everyone’s ideal temperature.
- You have rooms that are rarely used, such as guest bedrooms or a formal dining room. With a 2 zone HVAC, you can set these areas to a more energy-efficient temperature when unoccupied, without sacrificing comfort in the parts of the home you use regularly. This directly helps save money.
- You notice significant temperature variations between rooms or find yourself constantly adjusting vents. This indicates your current system struggles to provide even conditioning, a problem zone hvac systems are designed to solve.
If your home or lifestyle aligns with several of these points, a 2 zone HVAC system, or even one with multiple zones, could be an excellent upgrade. It offers a path to customizable heating and cooling, better energy management, and enhanced overall comfort for your indoor air. Consulting with an HVAC professional can help you determine the feasibility and potential benefits for your specific property, considering factors like ductwork, existing hvac units, and your goals for improved air quality and temperature control. They can also discuss whether a dual-zone air conditioner or a system catering to both heating and cooling is more appropriate. Some professionals may also offer related services such as furnace maintenance, heat pump maintenance, or even advice on tankless water heaters for comprehensive home energy solutions.
For those considering efficiency upgrades, comparing different types of systems can be useful. Below is a simple table outlining key differences:
| Feature | Single-Zone HVAC | 2-Zone HVAC System |
|---|---|---|
| Thermostats | One for the entire house. | Two (one for each zone). |
| Temperature Control | Uniform temperature target for all areas. | Independent temperature settings for each zone. |
| Energy Efficiency | Can be less efficient if some areas are over-conditioned or if unused spaces are fully conditioned. | Generally more efficient by conditioning only occupied or needy zones, reducing utility bills. |
| Comfort Level | May result in hot/cold spots; less personalized comfort. | Higher, more personalized comfort by addressing specific needs of each zone. |
| Upfront Cost | Lower installation cost. | Higher installation cost due to additional components like dampers and a control panel. |
| Ideal For | Smaller, single-story homes with uniform heating/cooling needs. | Multi-story homes, homes with distinct usage patterns, or varying heating/cooling loads in different areas. |
This comparison highlights how dual zone hvac systems provide more granular control. While the initial investment for zone hvac systems might be higher, the long-term benefits in comfort and energy savings often justify the cost, especially in homes well-suited for this technology. Thinking about other comfort systems, like gas fireplaces for supplemental heat or ductless air units for specific problem rooms, can also be part of a larger home comfort strategy. Proper pump maintenance for any hydronic components or sump pumps is also crucial for a healthy home environment.
Conclusion
Understanding how a 2 zone HVAC system works illuminates a path to smarter home climate management. These sophisticated HVAC systems offer precise control over your home’s temperature by creating distinct zones, each managed by its own thermostat. This approach can significantly contribute to energy savings on your monthly utility bills and a notable improvement in overall comfort levels throughout your home.
At its core, a 2 zone HVAC system utilizes a network of dampers within your ductwork, a central zone control panel, and multiple thermostats to intelligently direct heated or cooled air. This allows you to set and maintain different temperatures in different areas, a feature particularly beneficial in multi-story houses or homes with diverse heating and cooling needs in various rooms like the living room versus bedrooms. The ability to avoid heating or cooling unused spaces is a key factor in its efficiency and ability to help you save money.
While the installation of such dual-zone HVAC systems requires professional expertise and ongoing maintenance is important for optimal performance, the long-term advantages are compelling. If you are seeking ways to enhance your home’s comfort, improve indoor air quality, and operate your heating and cooling more efficiently, exploring a 2 zone HVAC system, or even systems with multiple zones, is certainly a worthwhile consideration for your HVAC systems needs.